The type of genetic material (DNA or RNA) and its structure (single or doublestranded, linear or circular, and segmented or nonsegmented) are used to classify the virus core structures (Table 2)) Table 2 Virus Classification by Capsid StructureAnswer (1 of 2) Many RNA's have a single strand — but a lot of double stranded structure That is because like proteins, many RNA's do a job, and form determines function, so that they have to have secondary structure (the double helix) and tertiary structure (the overall 3DFigure 2 (a) DNA is typically double stranded, whereas RNA is typically single stranded (b) Although it is single stranded, RNA can fold upon itself, with the folds stabilized by short areas of complementary base pairing within the molecule, forming a threedimensional structure

Understanding The Mechanical Response Of Double Stranded Dna And Rna Under Constant Stretching Forces Using All Atom Molecular Dynamics Pnas
How to make double stranded rna
How to make double stranded rna-A helical doublestranded structure A planar singlestranded structure A helical singlestranded structure RNA bases cannot basepair with one another A planar doublestranded structure uracil guanine There are several cellular processes that involve the formation of doublestranded RNA When doublestranded RNA forms, the base A can hydrogenDoublestranded RNA viruses (dsRNA viruses) are a polyphyletic group of viruses that have doublestranded genomes made of ribonucleic acidThe doublestranded genome is used to transcribe a positivestrand RNA by the viral RNAdependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) The positivestrand RNA may be used as messenger RNA (mRNA) which can be translated into viral




Structural Basis For Double Stranded Rna Processing By Dicer
Double stranded rna virus structure21 RNA viruses The genome of many RNA viruses is ssRNA, whereas the genome of others, such as reovirus, is doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) Furthermore, ssRNA viruses are classified as positive and negativesense ssRNA viruses that have positivesense (mRNAsense) and negativesense (antisense) RNA genomesIn a double stranded RNA form, retroviruses infect a host cell with their genome, and then are reverse transcribed into double stranded DNA, with the DNA then integrated into the home cell genome When integrated into a host genome, a retrovirus is hard to detect and can lay dormant for prolonged periods, having no discernible effect on the hostRNA interference (RNAi) is a genetic regulatory system that functions to silence the activity of specific genes RNAi occurs naturally, through the production of nuclearencoded premicroRNA (premiRNA), and can be induced experimentally, using short segments of synthetic doublestranded RNA (dsRNA)
Double stranded form could assume a ZDNA structure b) If the singlestranded molecule has the sequence 5'(GATC)10, then its doublestranded form could assume an HDNA structure c) If the singlestranded molecule has the sequence 5'(CTGA)10, then its doublestranded form could assume a hairpin structureComplementary basepairing is possible for RNA As the poster is no doubt aware, the doublestranded structure of DNA is stabilized by A–T and G–C base pairs He will also be aware that in transcription of DNA to RNA (in which A is replaced by U) A–U base pairing occurs Hence, there is no physicochemical reason why dsRNA cannot occur between suitable complementary strandsThe secondary structure of RNA is necessary for its maturation, regulation, processing, and function However, the global influence of RNA folding in eukaryotes is still unclear Here, we use a highthroughput, sequencingbased, structuremapping approach to identify the paired (doublestranded RNA
Thomis et al, 1992), Drosophila staufen protein (St Johnston et alMost cellular RNA is single stranded, although some viruses have double stranded RNA The single RNA strand is folded upon itself, either entirely or in certain regions In the folded region a majority of the bases are complementary and are joined by hydrogen bonds This helps in the stability of the molecule In theThe findings and conclusions of the experiment were ________ A mice died as a result of incorporation of DNA into the mouse genome from heatkilled smooth cells B mice survived as a result of a transforming agent picked up by the rough cells from the smooth cell extract C mice died as a result of a transforming agent picked up by the




Crystal Structure Of The 2 Specific And Double Stranded Rna Activated Interferon Induced Antiviral Protein 2 5 Oligoadenylate Synthetase Molecular Cell



Structure Dynamics And Rox2 Lncrna Binding Of Tandem Double Stranded Rna Binding Domains Dsrbd1 2 Of Drosophila Helicase Maleless
RNA By Himanshu Dev VMMC &O The DNA base pairs are more closely hydrogen bonded in the centre (left) due to the absence of the 2prime hydroxyl group in deoxyribose, and therefore double stranded DNA is not as bulky as RNA (right) ODNA has the nucleotide thymine, whereas RNA has uracil, which is bulkier than thymine and accounts for the broader RNA structureRNA interference (RNAi), a predominantly eukaryotic posttranscriptional regulatory mechanism, is the use of a cell's propensity to destroy doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules In RNAi, even singlestranded RNA that matches the dsRNA sequence is destroyed, thus effectively silencing a gene by regulating its expression posttranscriptionally



3



Poly I C Hmw Synthetic Dsrna Invivogen
RNA is a kind of molecule that is reproduced from DNA However, because of its singlestranded structure rather than a doublestranded structure, it is possible for RNA to reproduce itself using processes that are similar to those employed by DNA in the process It is believed that RNA reproduced itself in this manner in the first cells However, in modern cells, all of the RNA isThe RNA affinity falls within the range observed for characterized RNA/protein complexes Overall, we describe in moleculardetail the interactions of SapA with heme and dsRNA and propose a role for SapA in the transport of di or tripeptidesSecondly, DNA is doublestranded while RNA is single stranded Thirdly, DNA is more structurally stable compared to RNA The comparably slight instability allows RNA to be flexible and more accessible and can thus fold into meaningful structures, a property that can be fully appreciated in the proteins RNA makes




Structural Basis For Dsrna Recognition Filament Formation And Antiviral Signal Activation By Mda5 Sciencedirect



Double Stranded Rna Recognition In Gene Silencing Pathway
Firstly, the 'information' part of DNA is the nitrogenous base, as opposed to the pentose sugar or the phosphate residues In a singlestranded molecule, this important part would be exposed to the cellular environment, providing more opportunity for it to be mutated by the variousCas13 endonuclease activity depends on the RNA local secondary structure with strong preference for singlestranded (SS) regions Hence, it becomes indispensable to identify the SS regions forThe chemical structure of RNA is very similar to that of DNA, but differs in three primary ways Unlike doublestranded DNA, RNA is a singlestranded molecule in many of its biological roles and consists of much shorter chains of nucleotides However, a single RNA molecule can, by complementary base pairing, form intrastrand double helixes, as in tRNA



Dna Wikipedia
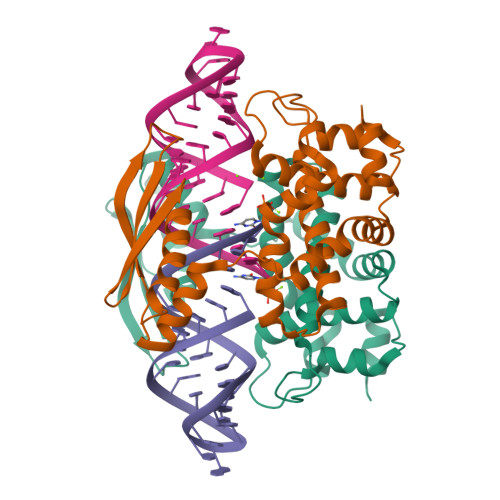



Rcsb Pdb 4m2z Crystal Structure Of Rnase Iii Complexed With Double Stranded Rna And Cmp Type Ii Cleavage
The overall structure of the double helix was compared with those of the canonical ARNA and A′RNA conformers (11 residues/turn for the Aform and 12 residues/turn for the A′form) The rmsd of the coordinates from the tridecamer duplex to ARNA and A′RNA are 160 and 113 Å, respectivelyStructure of the doublestranded RNAbinding domain of the protein kinase PKR reveals the molecular basis of its dsRNAmediated activation Sambasivarao Nanduri Structural Biology Program, Lerner Research Institute, The Cleveland Clinic Foundation, 9500 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, OH, USADoublestranded RNA Viruses Structure and Molecular Biology Edited by John T Patton Laboratory of Infectious Diseases, NIAID, NIH, Bethesda, MD , USA Published January 08 Pages x 374 Hardback ISBN £159, $319 Published by Caister Academic Press wwwcaistercom




Structure Of The Arabidopsis Thaliana Dcl4 Duf2 Domain Reveals A Noncanonical Double Stranded Rna Binding Fold For Protein Protein Interaction
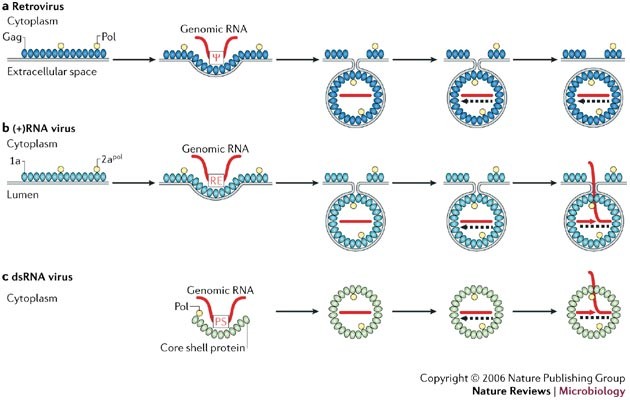



Parallels Among Positive Strand Rna Viruses Reverse Transcribing Viruses And Double Stranded Rna Viruses
Resolution, which reveals the mechanism of cytoplasmic dsRNA recognition andThe apparent affinity of the antibodies to short (less than or equal to 11 bp) RNA helices was very low in all test systems used only background levels of binding were obtained on singlestranded RNA species which contain doublehelical secondary structures (eg rRNA, tRNA, viroid RNA)Structure Of DNA &
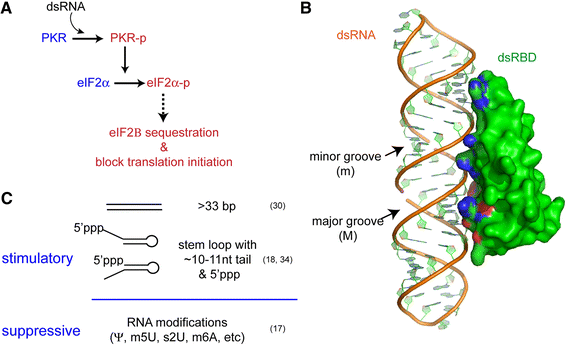



Multi Level Regulation Of Cellular Recognition Of Viral Dsrna Springerlink
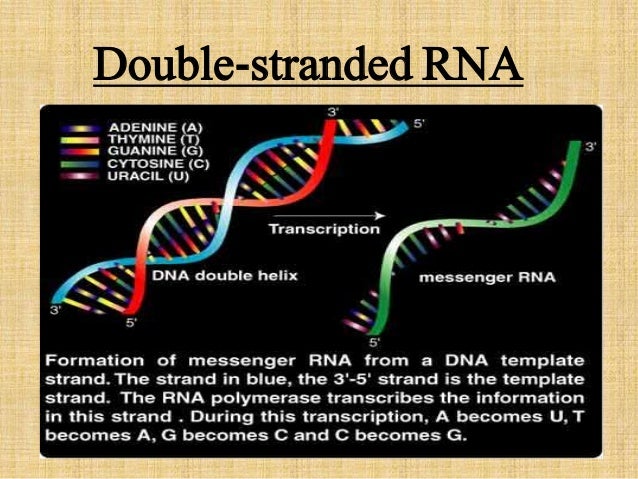



Structure Types And Function Of Rna
Virusspecific dsRNA is also found in cells infected with singlestranded RNA virusesDsRNA has been identified in a variety of apparently normal eucaryotic cells and isDouble stranded RNA, also known as dsRNA, usually shows up in viruses and is somewhat unusual In viruses, it is a unique characteristic, and only a small number of viral families exhibit this trait RNA hybridization happens when one RNA strand combines, or hybridizes, with either another RNA strand or a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) strandSJH DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA a polymer of deoxyribonucleotides Usually double stranded And have doublehelix structure found in chromosomes, mitochondria and chloroplasts It acts as the genetic material in most of




Fig 1 Structural Basis Of Toll Like Receptor 3 Signaling With Double Stranded Rna Science




Double Stranded Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Technology (21) DOI 10Differences between RNA and DNA SNo RNA DNA 1) Single stranded mainly except Double stranded (Except for when self complementary certain viral DNA s which are sequences are there it forms a single stranded) double stranded structure (Hair pin structure) 2) Ribose is the main sugar The sugar moiety is deoxy ribose 3) Pyrimidine components differRNA Interference (RNAi) Introduction RNA interference or PostTranscriptional Gene Silencing is a conserved biological response to doublestranded RNA that mediates resistance to both endogenous parasitic and exogenous pathogenic nucleic acids, and regulates the expression of proteincoding genesThis natural mechanism for sequencespecific gene silencing
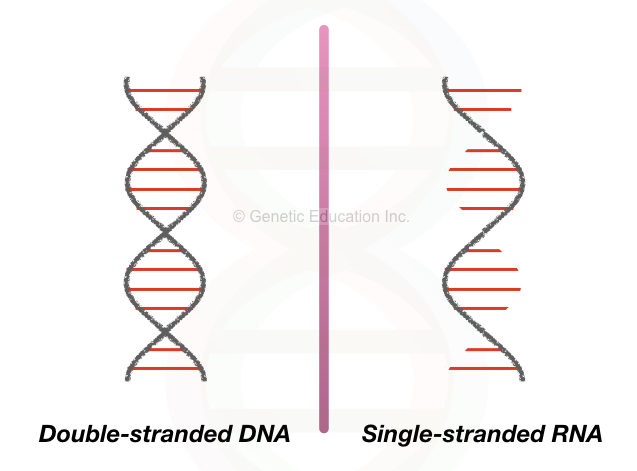



Dna Vs Rna Differences And Similarities




Analysis Of Double Stranded Rna From Microbial Communities Identifies Double Stranded Rna Virus Like Elements Sciencedirect
Welcome to the Predict a Secondary Structure Web Server The Predict a Secondary Structure server combines four separate prediction and analysis algorithms calculating a partition function, predicting a minimum free energy (MFE) structure, finding structures with maximum expected accuracy, and pseudoknot predictionThis server takes a sequence, either RNADouble stranded RNA binding proteins (dsRBPs) in particular are crucial for RNA interference, mRNA elongation, AtoI editing, host defense, splicing, and a multitude of other important mechanisms Since dsRBPs require doublestranded RNA to bind, their binding affinity depends on the competition among all possible secondary structures of theRNA Function Replicates and stores genetic information like a blueprint The main function of RNA is to carry information of amino acid sequence from the genes to where proteins are assembled on ribosomes in the cytoplasm Structure Doublestranded helix Single Stranded Structure Length DNA is a much longer polymer than RNA




Tdp 1 The Caenorhabditis Elegans Ortholog Of Tdp 43 Limits The Accumulation Of Double Stranded Rna The Embo Journal
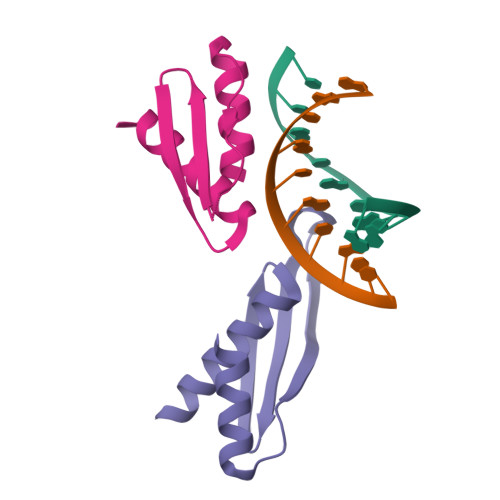



Rcsb Pdb 1di2 Crystal Structure Of A Dsrna Binding Domain Complexed With Dsrna Molecular Basis Of Double Stranded Rna Protein Interactions
DoubleStranded RNA Production of doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) is a part of the coxsackievirus replication cycle It has been shown that dsRNA is able to directly stimulate a dsRNctivated protein kinase (PKR) A major substrate of PKR is the α subunit of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2α)The key difference between DNA and RNA structure is that the DNA structure is a double helix composed of two complementary strands while RNA structure is singlestranded Nucleic acids are macromolecules or biopolymers Moreover, they are the building blocks of genetic material of an organism They are comprised of nucleotide chains linked via phosphodiesterRNA The secondary structure of RNA consists of a single polynucleotide RNA can fold so that base pairing occurs between complementary regions RNA molecules often contain both single and doublestranded regions The strands are antiparallel and assume a helical shape The helices are of the Aform (see above)




Structural Insight Into The Mechanism Of Double Stranded Rna Processing By Ribonuclease Iii Cell




Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology
The doublestranded RNAbinding domain (dsRBD) is a 6570 amino acid sequence/structure motif that mediates dsRNA interactions in a large variety of proteins (St Johnston et al, 1992) such as the dsRNAdependent protein kinase PKR (Meurs et al, 1990;More information Ke Zhang et al, Duplex Structure of DoubleStranded RNA Provides Stability against Hydrolysis Relative to SingleStranded RNA, Environmental Science &Up to12%cash backHigh molecular weight, fully doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) has been recognized as the genetic material of many plant, animal, fungal, and bacterial viruses (Diplomaviruses);




Crispr Csy4 Mediated Editing Of Rotavirus Double Stranded Rna Genome Sciencedirect




Understanding The Mechanical Response Of Double Stranded Dna And Rna Under Constant Stretching Forces Using All Atom Molecular Dynamics Pnas
The human sensor of doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) oligoadenylate synthetase 1 (hOAS1) polymerizes ATP into 2′,5′linked isoRNA (25A) involved in innate immunity, cell cycle, and differentiation We report the crystal structure of hOAS1 in complex with dsRNA and 2′deoxy ATP at 27 ÅRNA, like DNA, can form double helices held together by the pairing of complementary bases, and such helices are ubiquitous in functional RNAs Here we apply external forces and torques to individual doublestranded RNA molecules to determine the mechanical properties and conformational transitions of these fundamental biological building blocks For small forces and torques, RNAThe structure resulting from this interaction between the minor groove and singlestranded RNA at helical junctions displays internal mobility, which may be a general feature of RNA pseudoknots that regulates their interaction with proteins or other RNA molecules




Rna Wikipedia




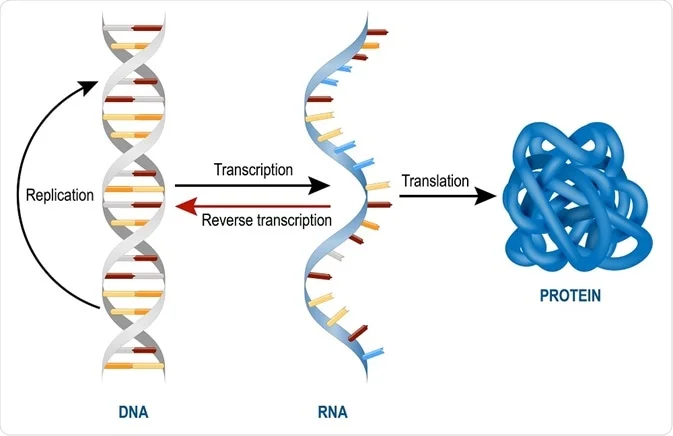
Dna And Rna Replication
In a double‐stranded DNA or RNA, this refers to the Watson‐Crick pairing of complementary strands In a single‐stranded RNA or DNA, the intramolecular base pairs between complementary base pairs determines the secondary structure of the molecule For example, the cloverleaf structure of Figure 2a gives the secondary structure of transferDNA forms a doublestranded helical structure that contains base pairs, whereas RNA is singlestranded and does not form base pairs or adopt a doublehelical conformation ThisGreen and Mathews, 1992;
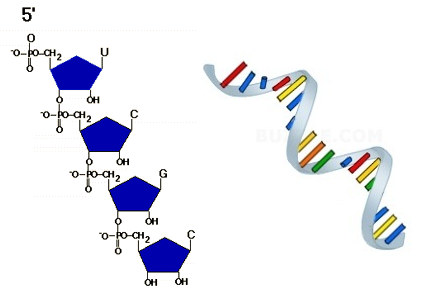



Structure Of Rna Single Stranded Structure And Its Classification




Solution Structure Of The Drosha Double Stranded Rna Binding Domain Semantic Scholar
Why is DNA double stranded (and not single stranded like RNA)?Mindich L Precise packaging of the three genomic segments of the doublestrandedRNA bacteriophage phi6 Microbiology and molecular biology reviews MMBR 63, 149–160 (1999) PMC free article Google Scholar Katz A et al Bacteriophage phi6–structure investigated by fluorescence Stokes shift spectroscopy
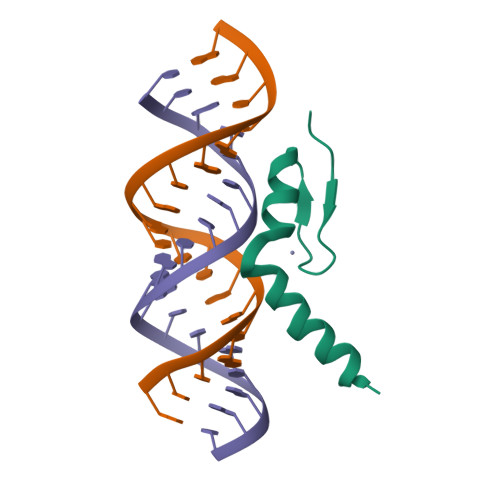



Rcsb Pdb 2mkn Structural Characterization Of Interactions Between The Double Stranded Rna Binding Zinc Finger Protein Jaz And Dsrna




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia



Cell Com
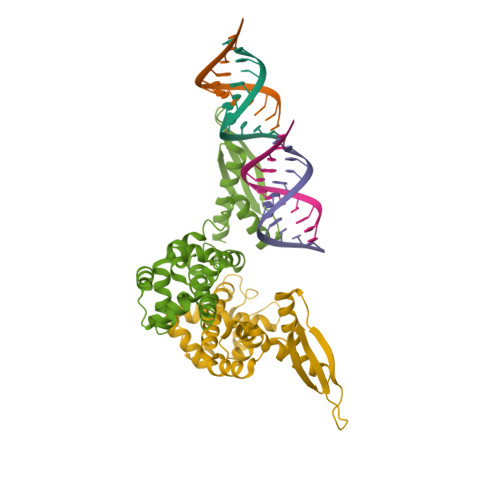



Rcsb Pdb 1yyw Crystal Structure Of Rnase Iii From Aquifex Aeolicus Complexed With Double Stranded Rna At 2 8 Angstrom Resolution



Rna Secondary Structure



1
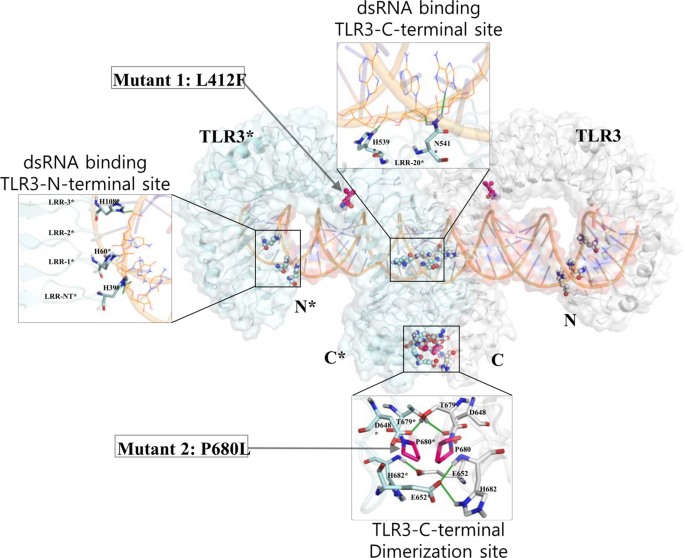



Insights Into The Dynamic Nature Of The Dsrna Bound Tlr3 Complex Scientific Reports




Rna Interference Overview Abcam
/DNAstructure-58c233583df78c353c23dbe6.jpg)



Nucleic Acids Function Examples And Monomers



2 The Basic Structure Of Dna And Rna Dna Is Double Stranded Whereas Download Scientific Diagram




Human Nlrp1 Is A Sensor For Double Stranded Rna




Structural Basis For Cytosolic Double Stranded Rna Surveillance By Human Oligoadenylate Synthetase 1 Pnas




Double Stranded Rna Single Stranded Dna Biology Stack Exchange
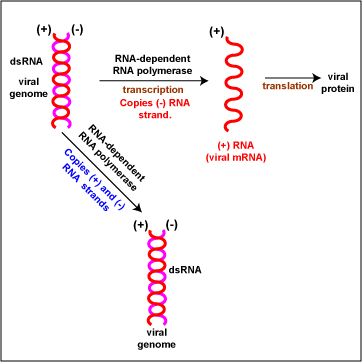



10 4 Classification Of Viruses Biology Libretexts




File Double Stranded Rna Gif Wikimedia Commons




Segmented Double Stranded Rna Viruses Structure And Molecular Biology Patton John T Amazon Com Books




Rna Virus Wikiwand




Structural Basis For Double Stranded Rna Processing By Dicer



What Is The Difference Between Dna And Double Stranded Rna Quora




File Difference Dna Rna En Svg Wikimedia Commons
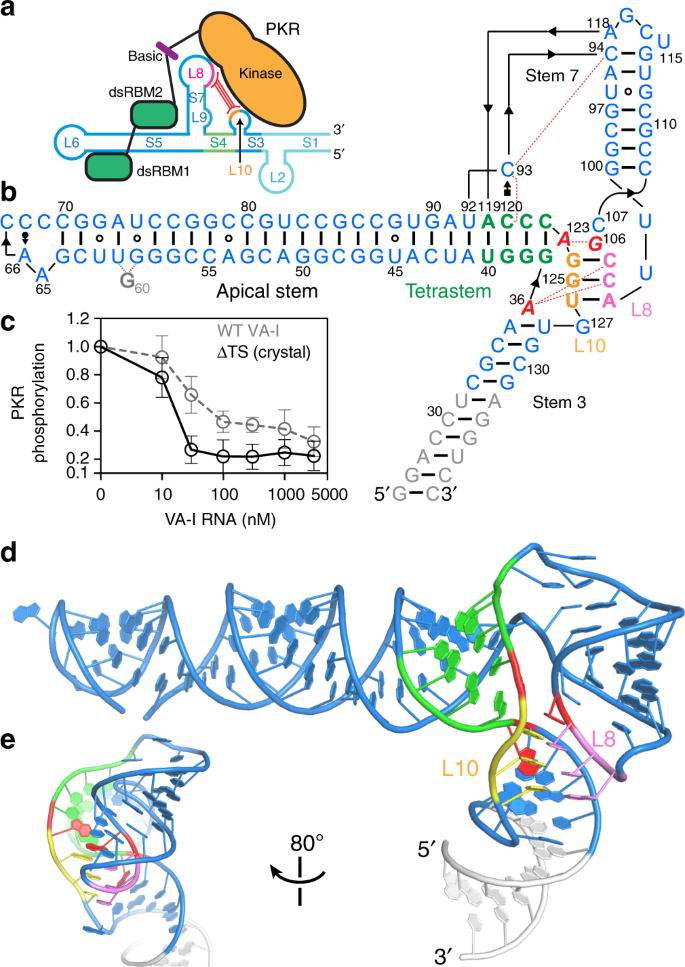



Crystal Structure Of An Adenovirus Virus Associated Rna Nature Communications
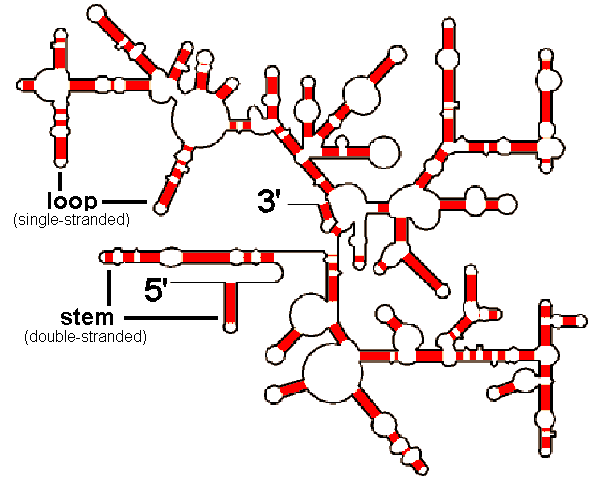



Stems Loops In Rrna
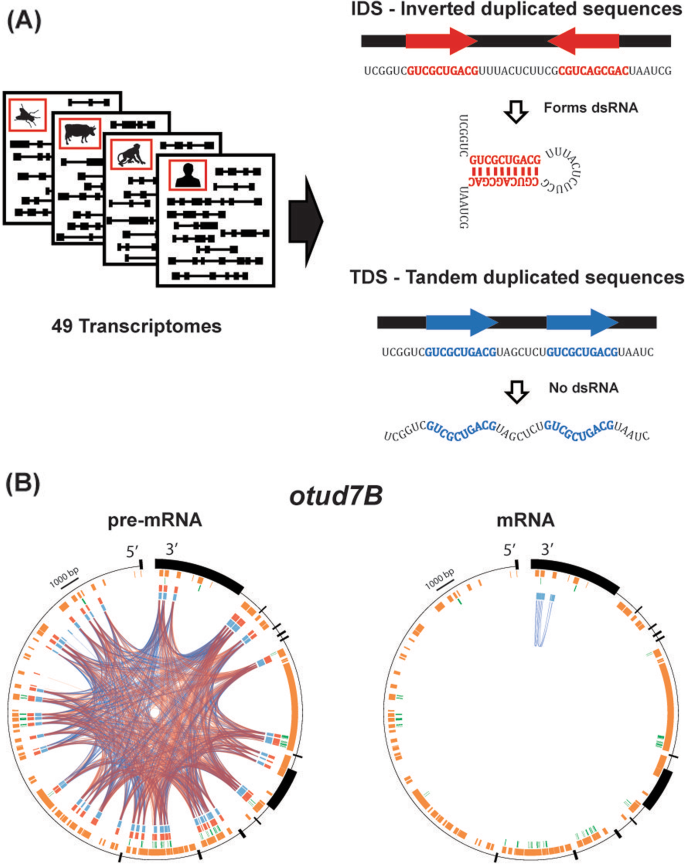



Purifying Selection Of Long Dsrna Is The First Line Of Defense Against False Activation Of Innate Immunity Genome Biology Full Text




5 Gcu Sites In Four Different Rna Secondary Structures Rna Was Download Scientific Diagram




Structures And Axis Curves For Ideal Dsdna And Dsrna Left Dna Right Download Scientific Diagram
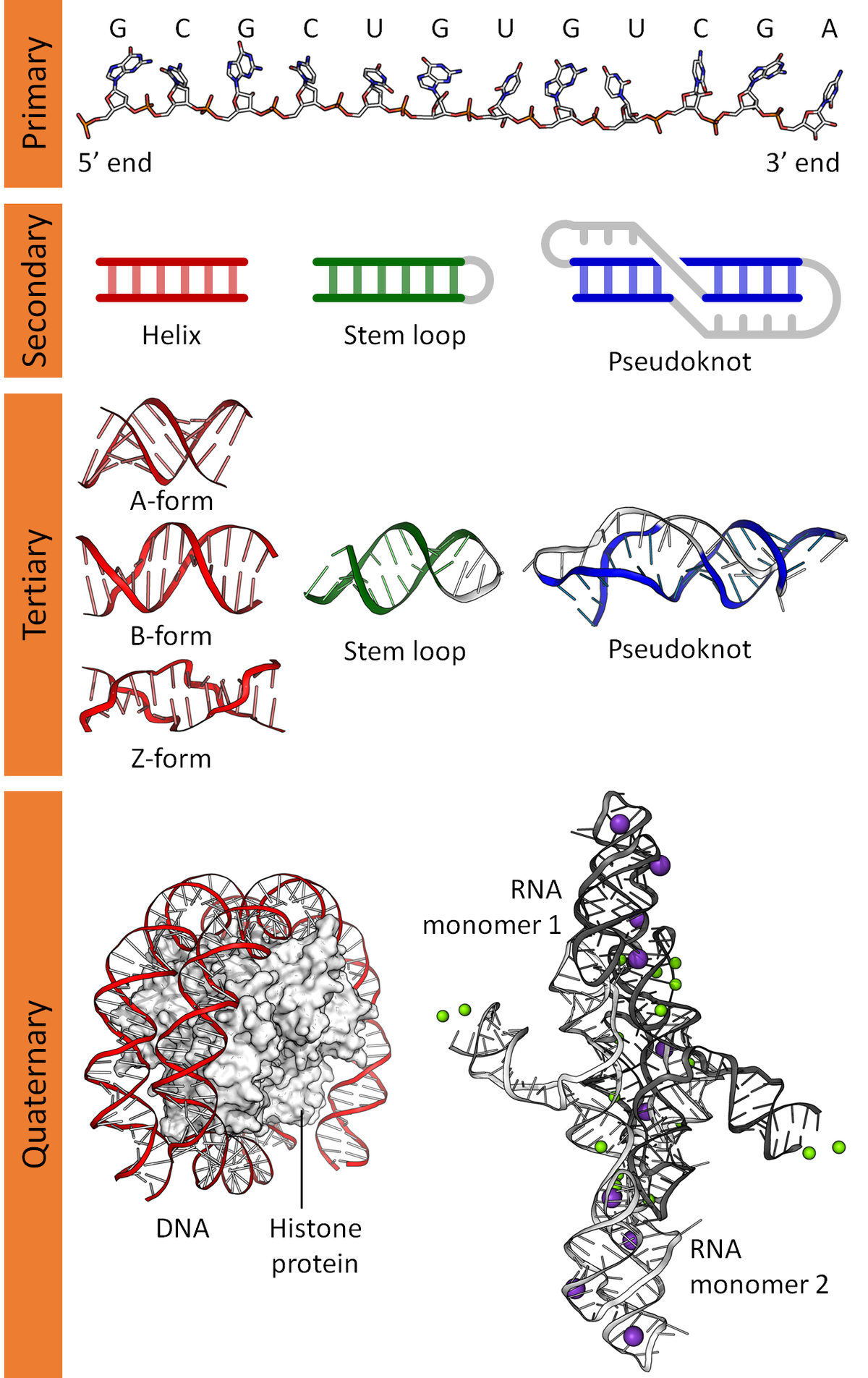



Nucleic Acid Structure Wikipedia




Double Stranded Rna Viruses Wikipedia
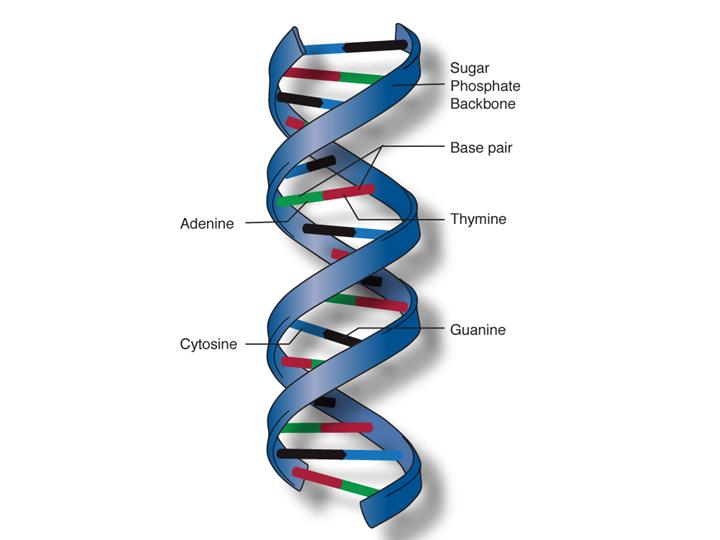



Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network




Rna Integrity And Quantification




Structural Basis For Double Stranded Rna Processing By Dicer
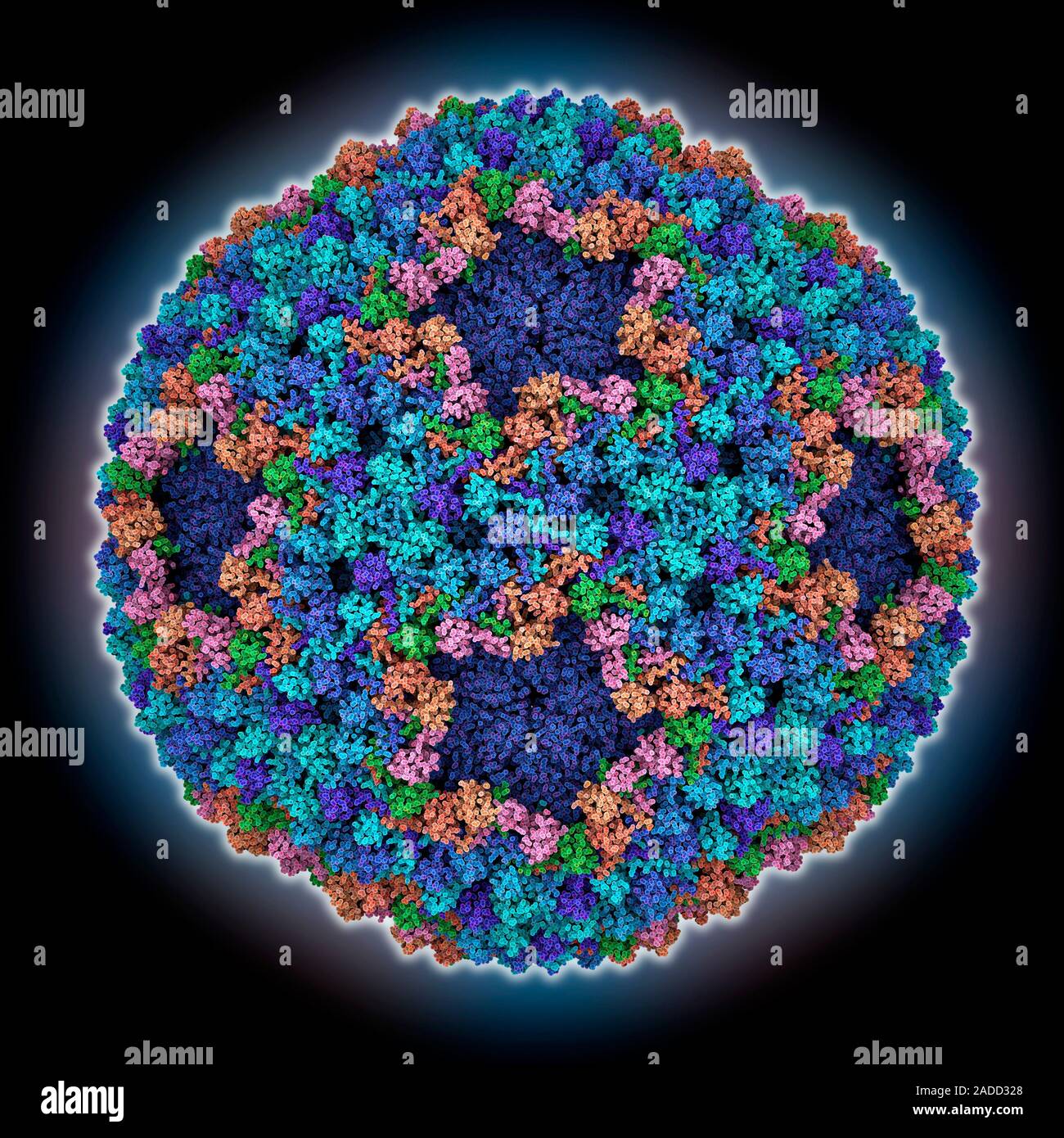



Bacteriophage Phi6 Virus Capsid Computer Model Showing The Structure Of A Double Stranded Rna Virus Bacteriophage Phi6 Capsid Stock Photo Alamy
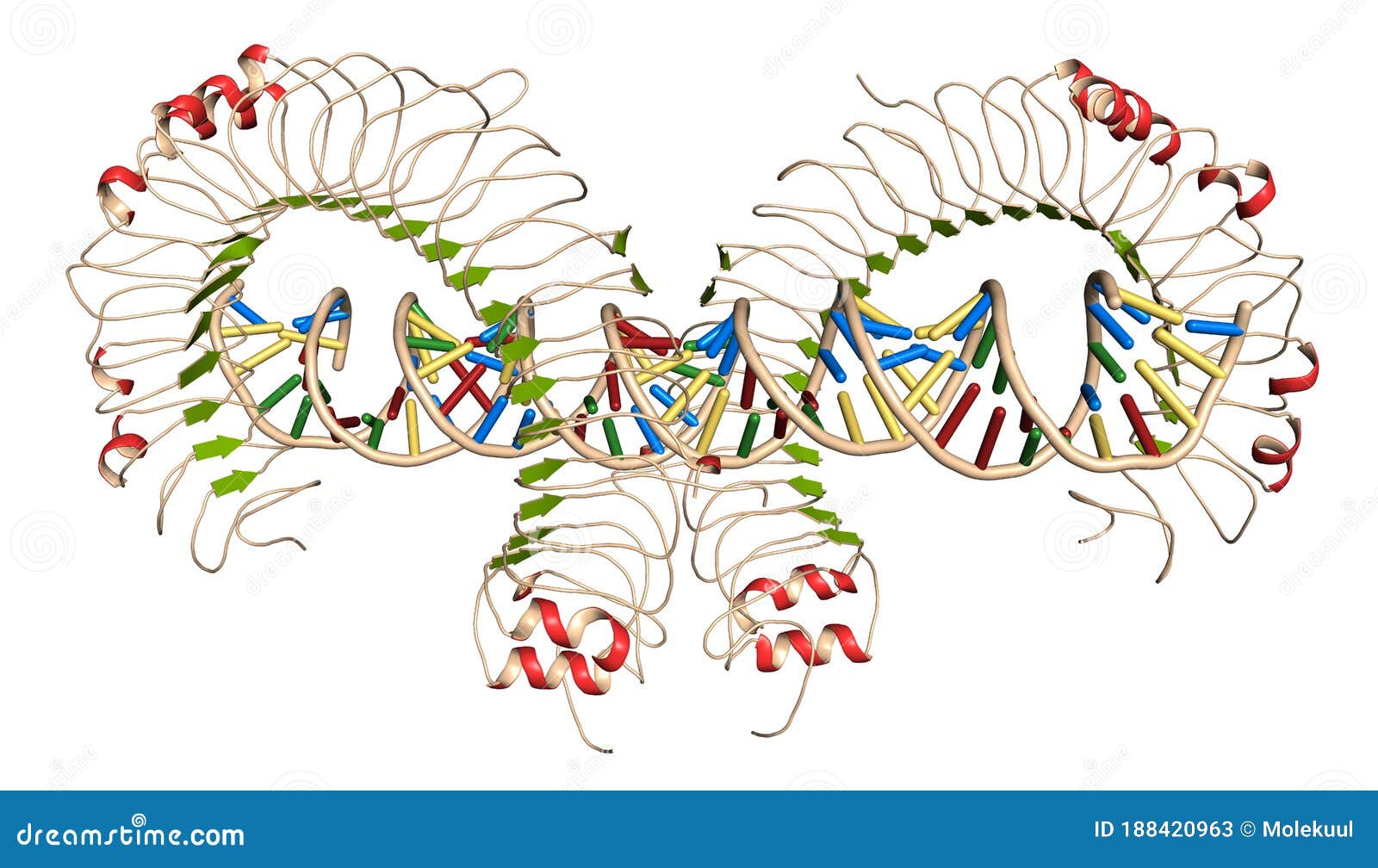



Toll Like Receptor 3 Tlr3 Murine Ectodomain Protein Bound To Double Stranded Rna Involved In Host Defense Against Viruses Stock Illustration Illustration Of Doublestranded Cd2
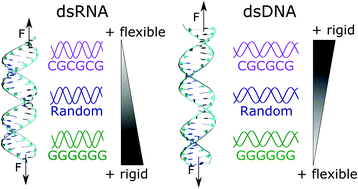



Sequence Dependent Mechanical Properties Of Double Stranded Rna Nanoscale Rsc Publishing



Types Of
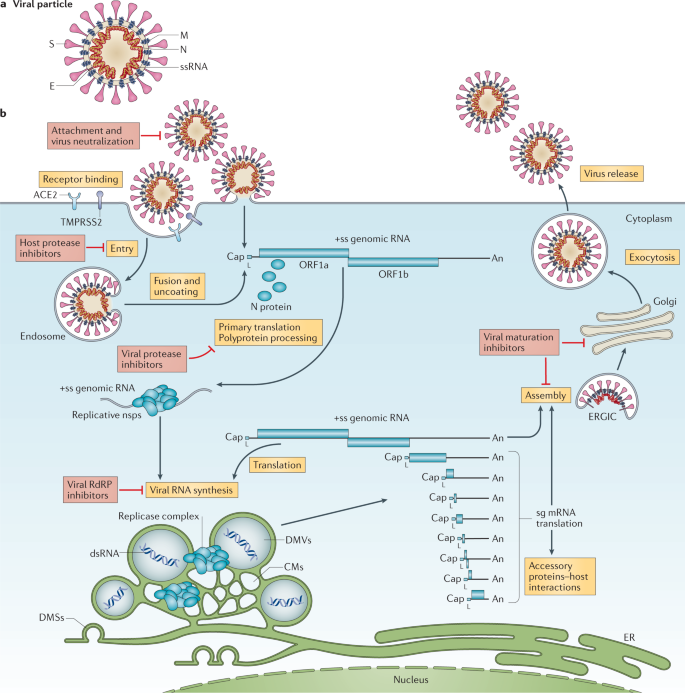



Coronavirus Biology And Replication Implications For Sars Cov 2




Iv Nuclear Biochemistry 4 2 Nucleic Acids 4



1
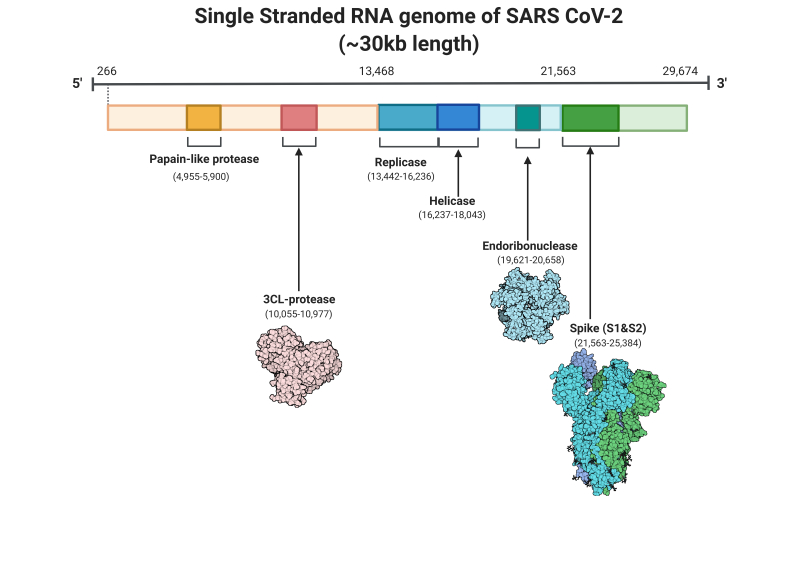



Figure Single Stranded Rna Genome Of Sars Cov2 Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Double Stranded Rna Binding Motif Dsrbm And Related Structures A Download Scientific Diagram




Figure 3 From Black Sheep That Don T Leave The Double Stranded Rna Binding Domain Fold Semantic Scholar
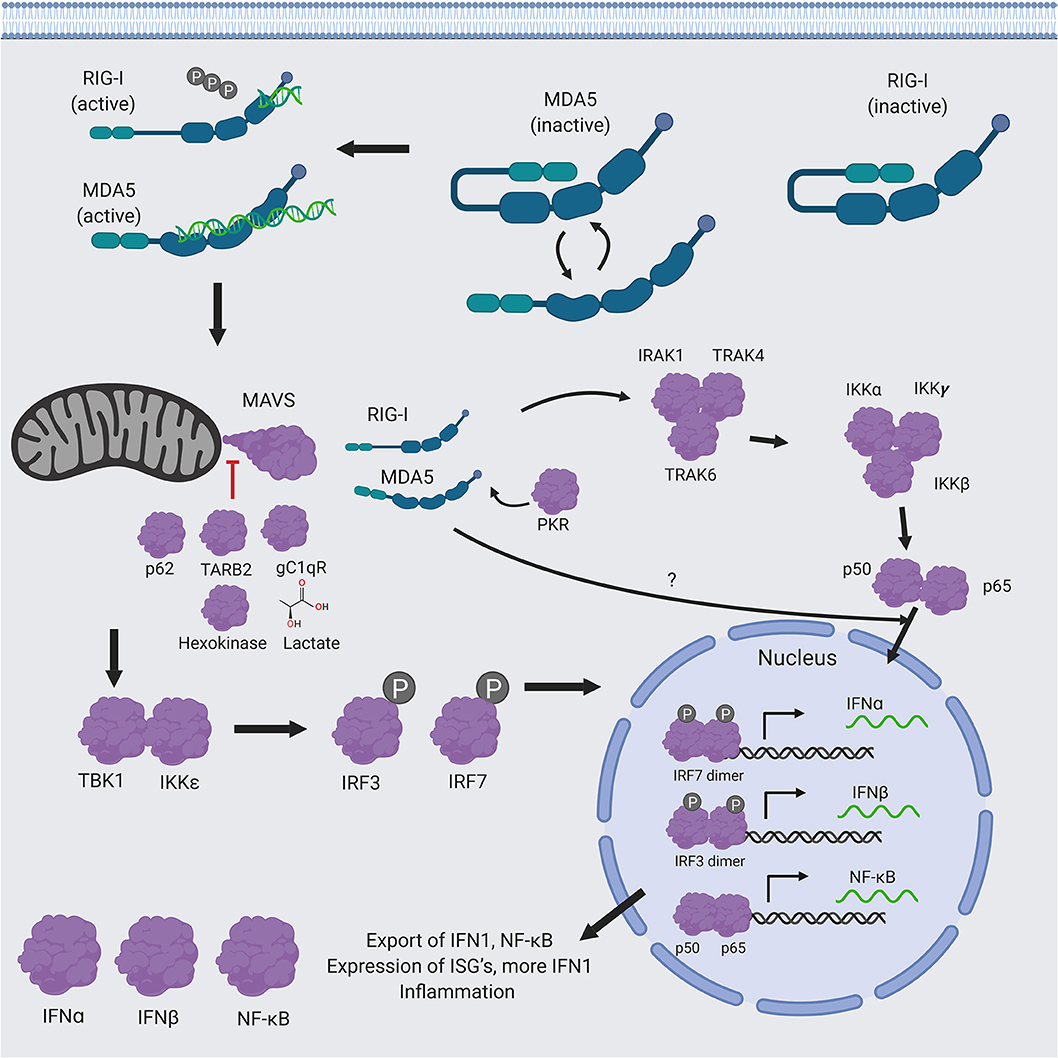



Frontiers Comparative Structure And Function Analysis Of The Rig I Like Receptors Rig I And Mda5 Immunology




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks




Understanding The Coronavirus Is Like Reading A Sentence Ieee Spectrum
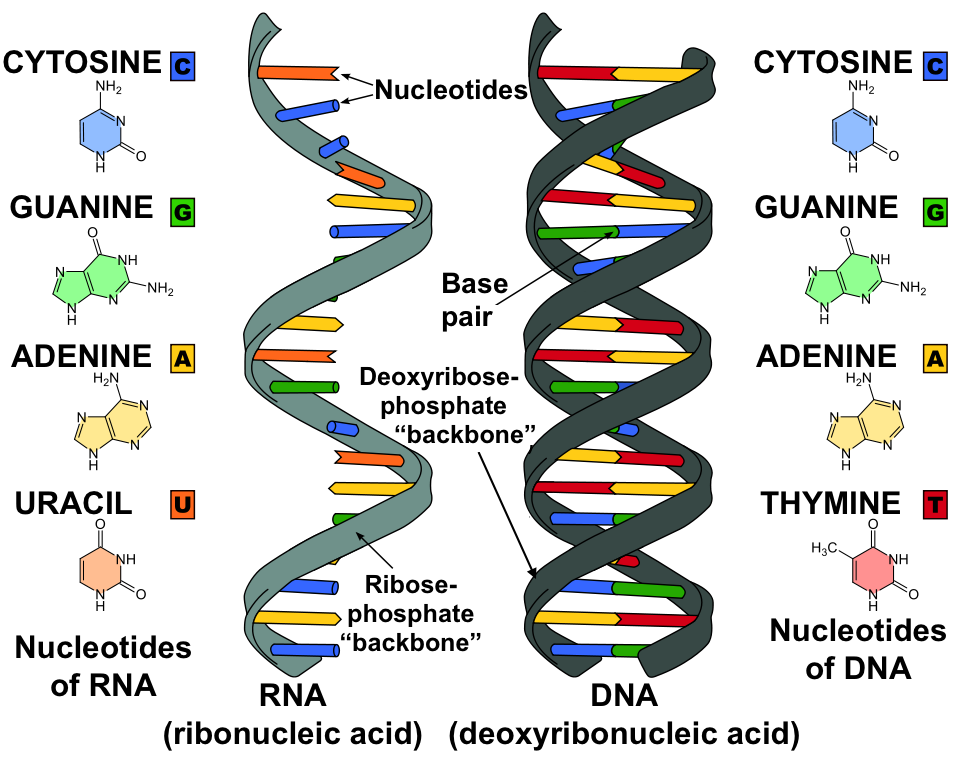



Rna And Protein Synthesis Review Artykul Khan Academy




Dna Vs Rna Vector Illustration Educational Genetic Acid Explanation Diagram Nucleobases Structure Labeled Scheme Ribonucleic And Deoxyribonucleic Molecule Helix Chain Differences Comparison Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration
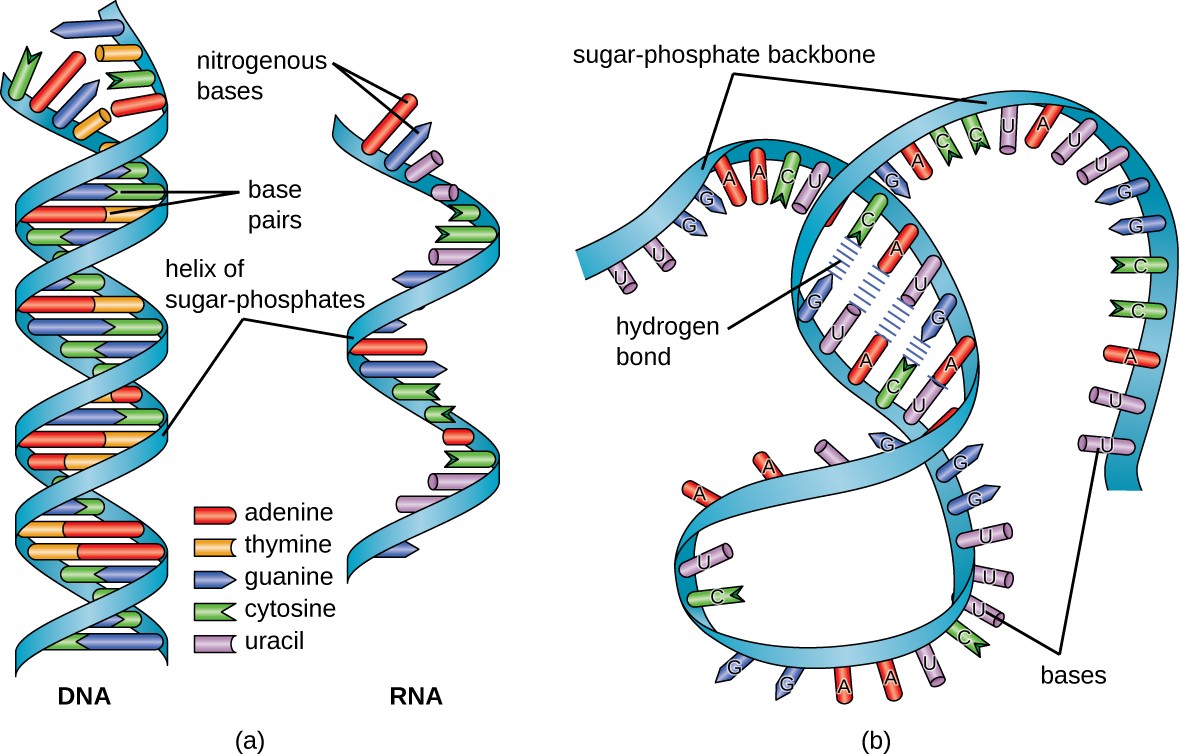



Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology
/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)



The Differences Between Dna And Rna



Plos Pathogens Acquisition Of Functions On The Outer Capsid Surface During Evolution Of Double Stranded Rna Fungal Viruses




Rna Virus Wikipedia




Structures And Axis Curves For Ideal Dsdna And Dsrna Left Dna Right Download Scientific Diagram
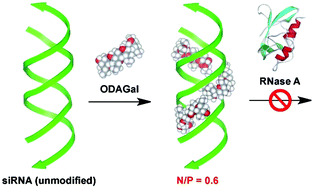



Double Stranded Rna Binding Artificial Cationic Oligosaccharides Stabilizing Sirnas With A Low N P Ratio Organic Biomolecular Chemistry Rsc Publishing
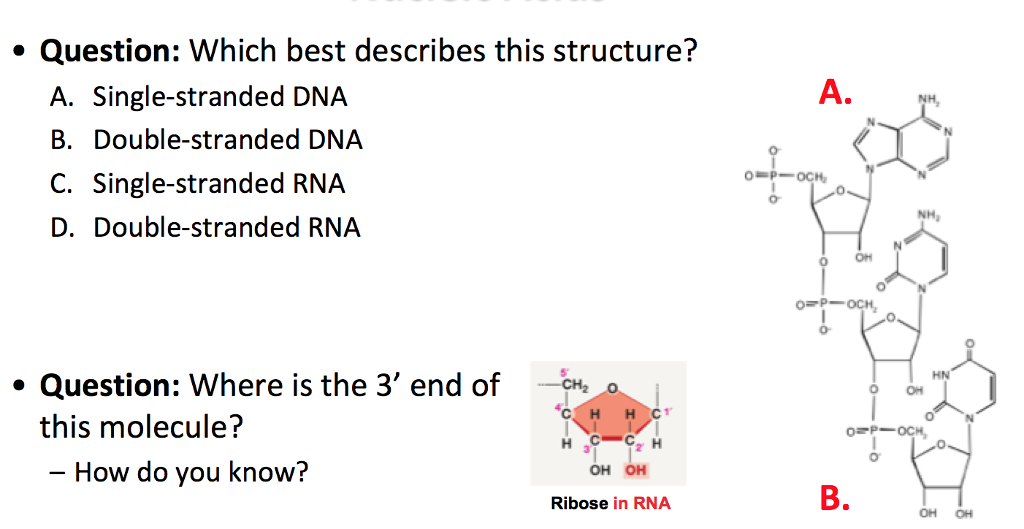



Solved Question Which Best Describes This Structure A Chegg Com
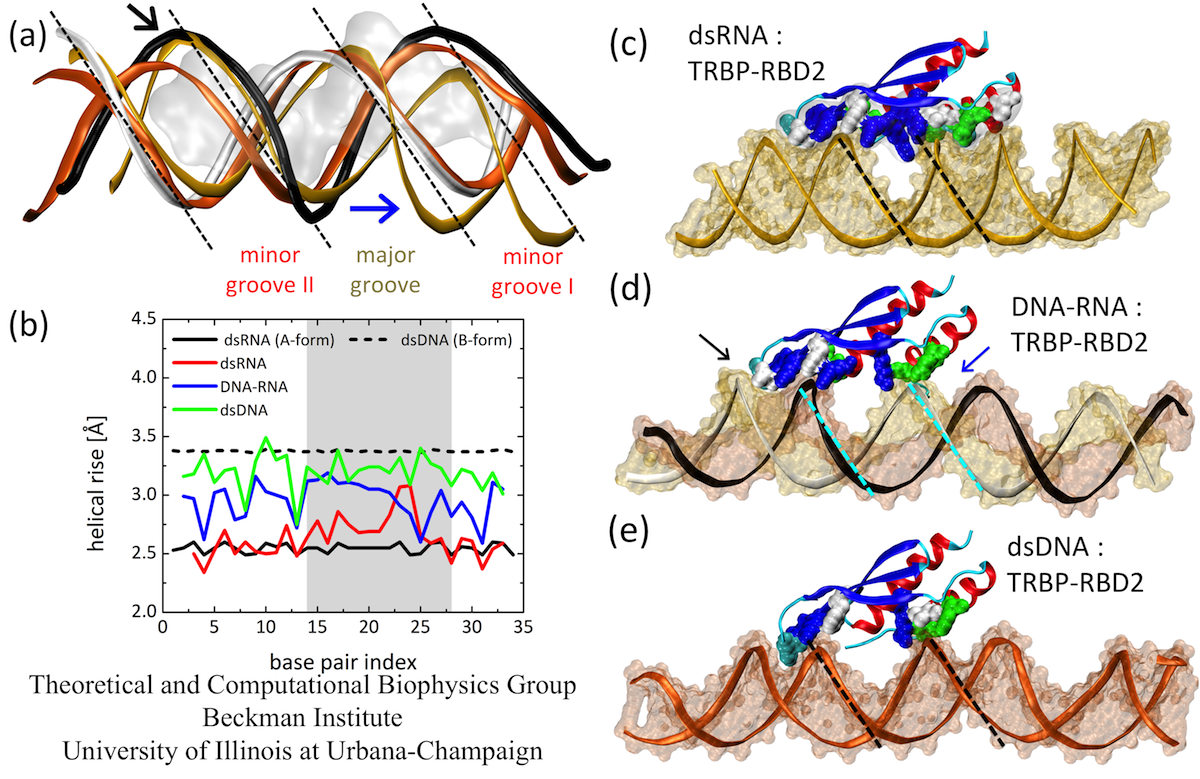



Double Stranded Rna Recognition In Gene Silencing Pathway




Characterization Of A Novel Megabirnavirus From Sclerotinia Sclerotiorum Reveals Horizontal Gene Transfer From Single Stranded Rna Virus To Double Stranded Rna Virus Journal Of Virology
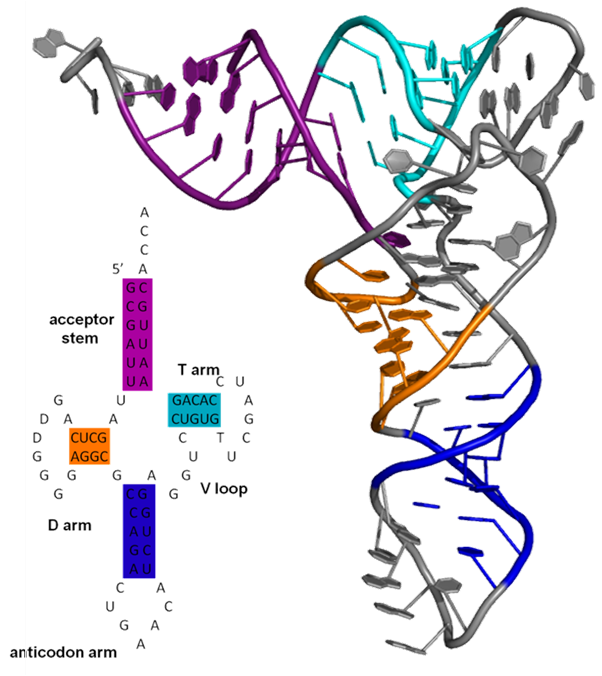



Rna Biomacromolecular Structures




Sars Cov 2 Induces Double Stranded Rna Mediated Innate Immune Responses In Respiratory Epithelial Derived Cells And Cardiomyocytes Pnas




Double Stranded Rna Biochemistry Britannica




Structure Of Hiv 1 Rt Dsrna Initiation Complex Prior To Nucleotide Incorporation Pnas
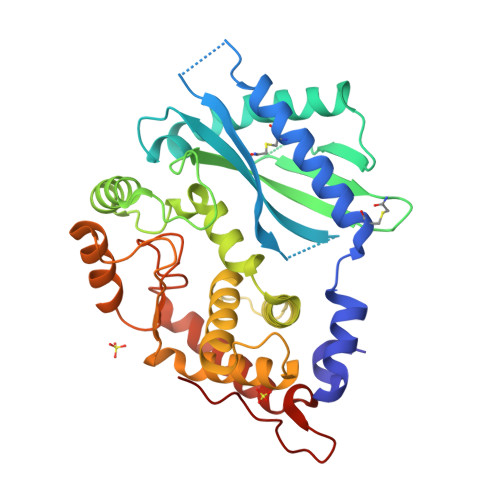



Rcsb Pdb 1px5 Crystal Structure Of The 2 Specific And Double Stranded Rna Activated Interferon Induced Antiviral Protein 2 5 Oligoadenylate Synthetase




Dna Vs Rna Similarities And Differences
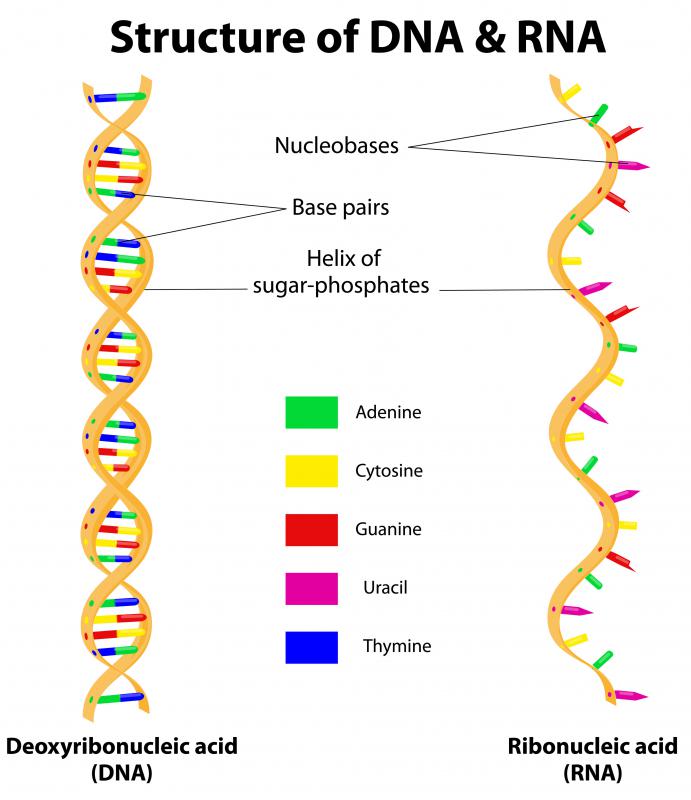



What Is Rna Interference With Picture




Functional Characterization Of And Cooperation Between The Double Stranded Rna Binding Motifs Of The Protein Kinase Pkr Journal Of Biological Chemistry




2 Dimensional Schematics Of The Double Strand Rna Structures Used In Download Scientific Diagram
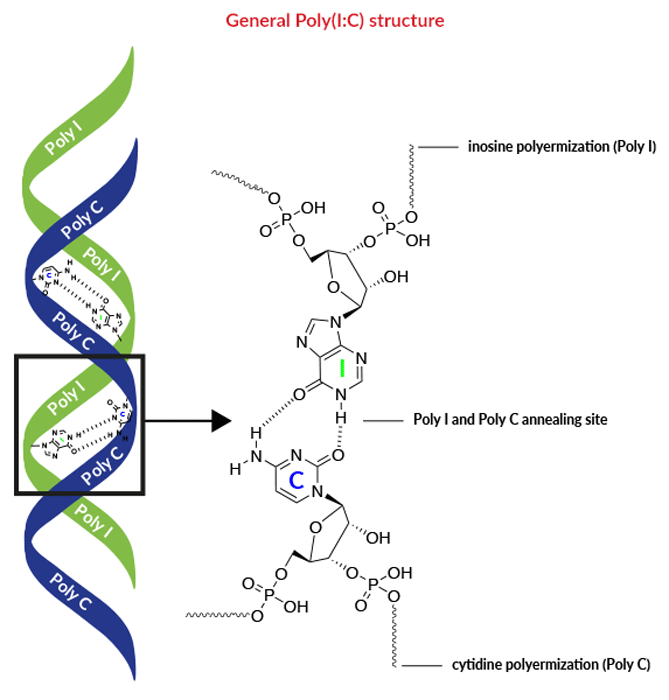



Tlr3 Ligands Synthetic Dsrna Poly I C Invivogen



Types Of Rna Mrna Rrna And Trna




The Chemical Structure Of Dna Compound Interest




Double Stranded Rna Under Force And Torque Similarities To And Striking Differences From Double Stranded Dna Pnas
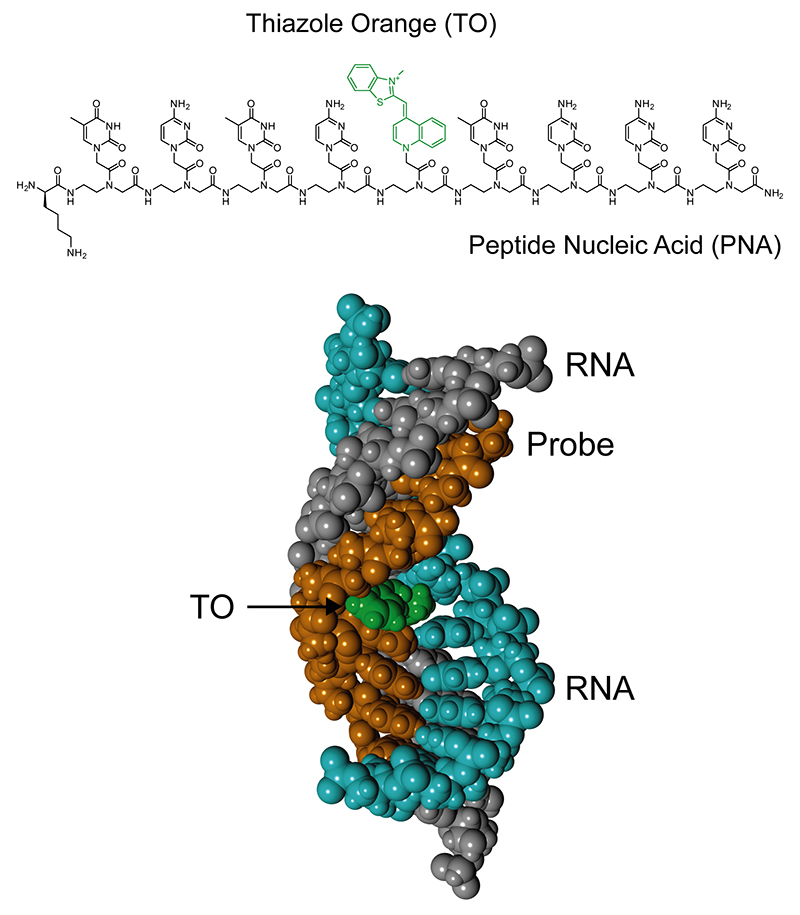



Research News New Analytical Tool For Fluorescence Detection Of Double Stranded Rna Tohoku University Global Site




Segmented Double Stranded Rna Viruses Structure And Molecular Biology
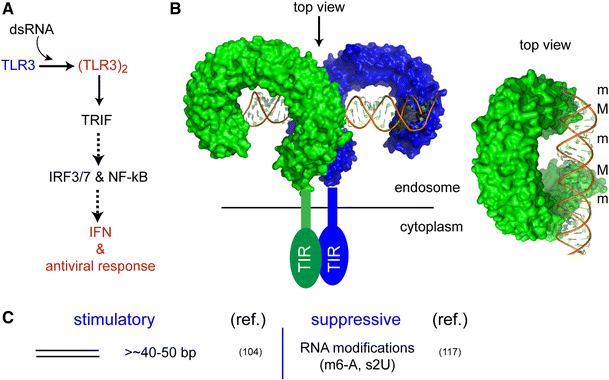



Multi Level Regulation Of Cellular Recognition Of Viral Dsrna Springerlink




Rna Double Helix Structure Identified Using Synchrotron Newsroom Mcgill University
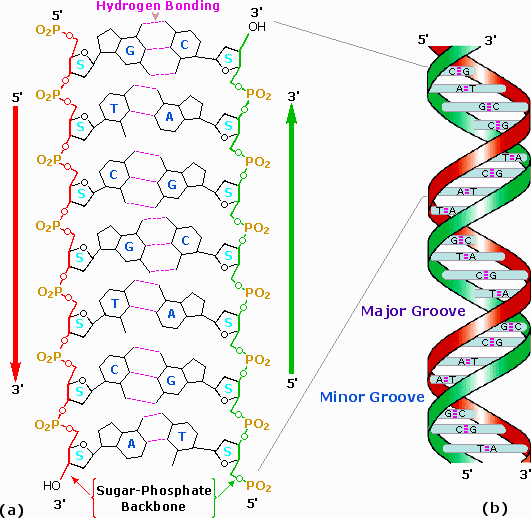



Nucleic Acids
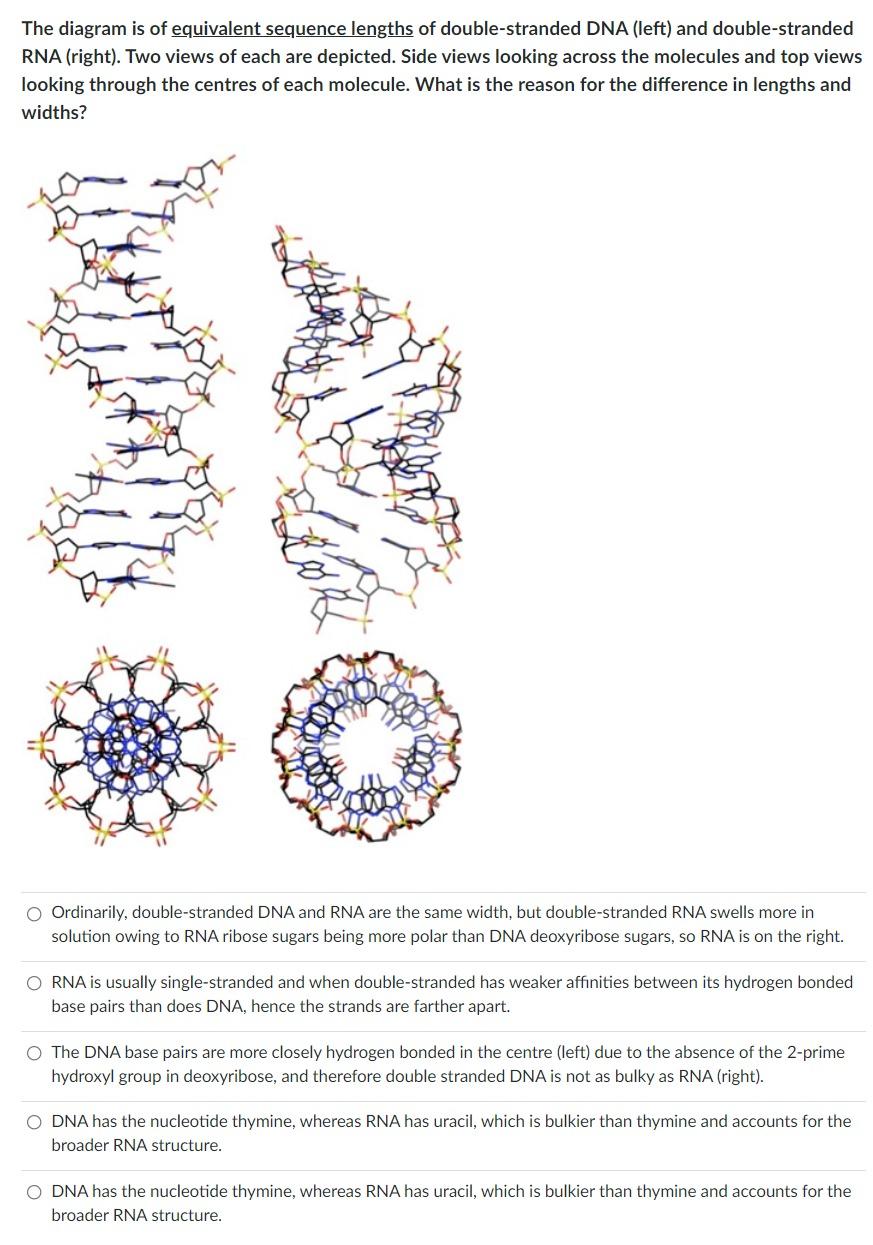



M4wg9h70l7e9om



Plos Biology Extensive Editing Of Cellular And Viral Double Stranded Rna Structures Accounts For Innate Immunity Suppression And The Proviral Activity Of Adar1p150




Structural Basis For Dsrna Recognition Filament Formation And Antiviral Signal Activation By Mda5 Sciencedirect




Nucleic Acid Structure Wikiwand
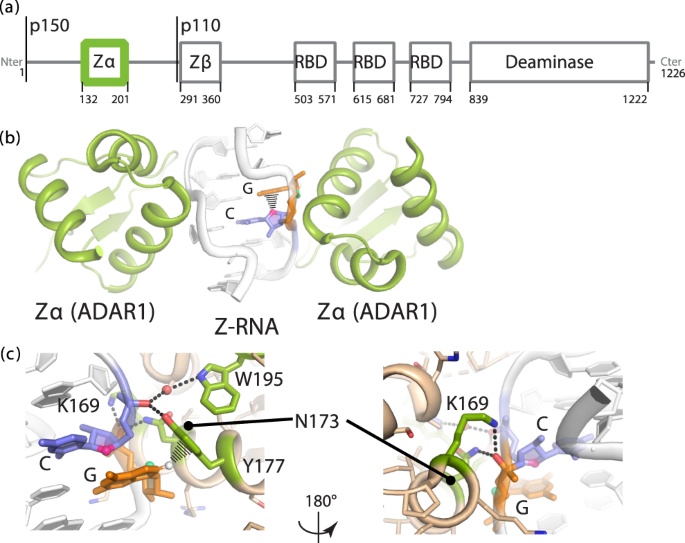



Recognition Of Non Cpg Repeats In Alu And Ribosomal Rnas By The Z Rna Binding Domain Of Adar1 Induces A Z Junctions Nature Communications




The Predicted 3d Structures Ballstick With Mean Minimal Rmsds In Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿